Problem Description
After installing nginx from source code, use the following code to register nginx as a system service:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
|
# Create service script
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
# nginx.service file content
[Unit]
Description=The NGINX HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=syslog.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# Reload configuration files
systemctl daemon-reload
# Start nginx service
systemctl start nginx
# Check nginx service status
systemctl status nginx
|
The image below shows the nginx service status after installing nginx from source code and adding nginx as a system service.
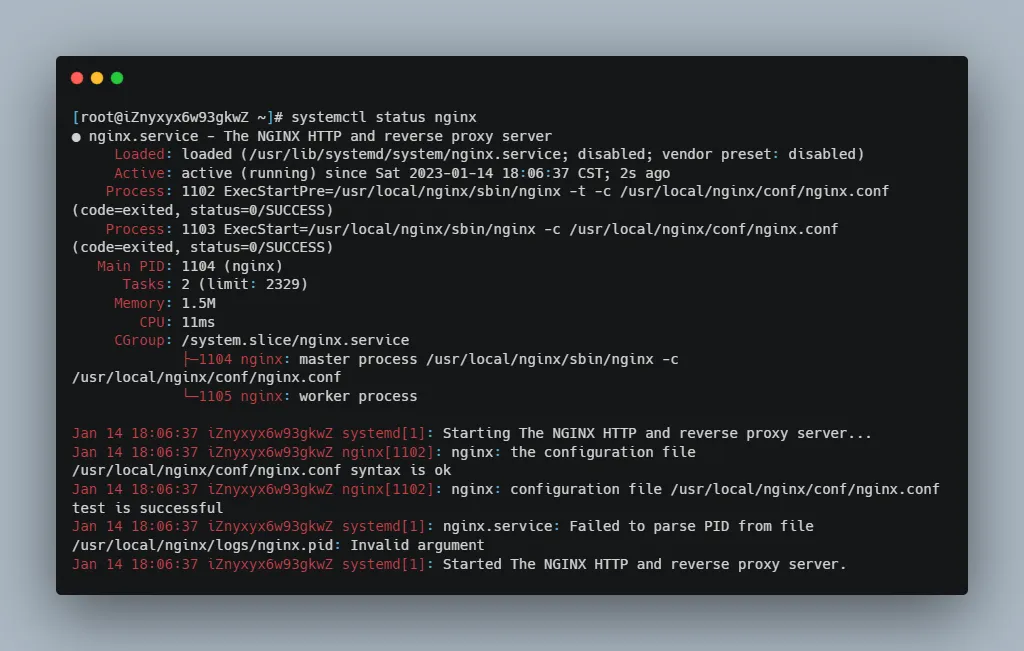
Focus on the second to last line. The error message is nginx.service: Failed to parse PID from file /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid: Invalid argument. This means parsing PID from file /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid failed.
The path /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid was defined in the nginx.service file’s [Service] section: PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid. The path is correct, which left me puzzled.
There’s discussion about a similar issue on Stack Overflow: centos 7: nginx Failed to read PID from file /run/nginx.pid: Invalid argument.
There are two answers. The first says the warning in the log can be ignored (indeed it can, because this error doesn’t cause nginx to malfunction). The second says restarting the server solved the problem. So I also restarted the server, but after restarting and checking nginx status, the error message changed to nginx.service: New main PID does not exist or is a zombie., meaning the new main process ID doesn’t exist or is a zombie process. So I restarted the nginx service, and after restarting, the error message changed back to the original one: nginx.service: Failed to parse PID from file /usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid: Invalid argument.
Solution
Finally, I solved the problem by combining the following 3 web pages:
nginx.service: Failed to read PID from file /run/nginx.pid: Invalid argument
Nginx.service: failed to parse pid from file /run/nginx.pid: invalid argument
nginx.service: Failed to parse PID from file /run/nginx.pid: Invalid argument
Solution: Add a new line ExecStartPost=/bin/sleep 0.1 in the nginx.service file’s [Service] section. This means after systemd starts the nginx service, it sleeps for 0.1s to ensure the nginx service has finished starting and created the PIDFile. This way, when systemd reads nginx’s PID, it won’t fail.
Note the new code line with + sign below:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
# Create service script
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/nginx.service
# nginx.service file content
[Unit]
Description=The NGINX HTTP and reverse proxy server
After=syslog.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
[Service]
Type=forking
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
+ ExecStartPost=/bin/sleep 0.1
ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
PrivateTmp=true
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
# Reload configuration files
systemctl daemon-reload
# Start nginx service
systemctl start nginx
# Check nginx status
systemctl status nginx
# Enable auto-start on boot
systemctl enable nginx.service
|
Explanation of service script content:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
|
# Define startup order and dependencies.
[Unit]
# Brief description of the current service.
Description=The NGINX HTTP and reverse proxy server
# Startup order.
After=syslog.target remote-fs.target nss-lookup.target
# Define how to start the current service.
[Service]
# Define startup type.
Type=forking
# Path to the service's PID file.
PIDFile=/usr/local/nginx/logs/nginx.pid
# Command to execute before starting service, -t tests config and exits, -c specifies config file.
ExecStartPre=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -t -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
# Command to execute when starting process, -c specifies config file.
ExecStart=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -c /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf
# Command to execute after starting service, sleep 0.1s before systemd reads PID file.
ExecStartPost=/bin/sleep 0.1
# Command to execute when restarting service, -s sends signal to main process.
ExecReload=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s reload
# Command to execute when stopping service, -s sends signal to main process.
ExecStop=/usr/local/nginx/sbin/nginx -s stop
# If true, sets up a new filesystem namespace for the executed process with a private /tmp directory
# mounted, which processes outside the namespace won't share.
# Useful for protecting access to process temp files, but can't share via /tmp between processes.
# Default is false.
PrivateTmp=true
# Define how to install this configuration file.
[Install]
# Indicates which Target this service belongs to.
WantedBy=multi-user.target
|
Summary

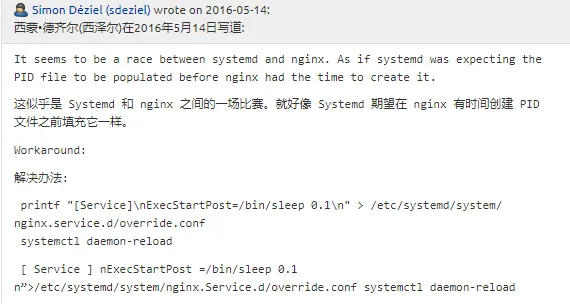
Image 1 source
Image 2 source


